
C. torulosa growing in habitat with Quercus floribunda and Q. oblongata near Nainital (India), elev. 2,084 m [Gaurav Verma, 2019.04].

Tree about 20 m tall at Yatton Park, Tauranga, New Zealand [C.J. Earle, 2003.03].

Branchlets and leaves from the above tree [C.J. Earle, 2003.03].

Seed cones from the above tree [C.J. Earle, 2003.03].

Bark on the above tree (ca. 80 cm diameter) [C.J. Earle, 2003.03].
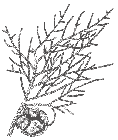
Cone-bearing branchlet with leaves and seed cone [Li Aili] (Fu et al. 1999).
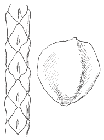
Branchlet with leaves, and seed [Li Aili] (Fu et al. 1999).

Cupressus torulosa
D.Don 1824
Common names
Bhutan cypress (Silba 1986), Himalayan cypress (Vidakovic 1991), Hoàng dàn [Vietnamese] (FIPI 1996), 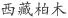 [Chinese] (Fu et al. 1999).
[Chinese] (Fu et al. 1999).
Taxonomic notes
Syn: Cupressus whitleyana Carr. 1855; Cupressus sempervirens L. var. indica Royle ex Parl. in Candolle 1868; Cupressus doniana hort. ex Hook. 1888; Cupressus karnaliensis Silba 1994; Cupressus tongmaiensis Silba 1994; Cupressus tongmaiensis var. ludlowii Silba 1994; Cupressus tongmaiensis var. mustangensis Silba 1994; Cupressus tonkinensis Silba 1994 (Farjon 1998); Cupressus flagelliformis Knight.; Cupressus nepalensis Loud.; Cupressus tournefortii Ten. (Vidakovic 1991).
Description
A evergreen tree 15-25(45) m tall, with a dbh of 40-60(90) cm. Crown large oval to broadly conical. Bark thick, grey brown or brown, peeling off in longitudinal strips. Branches slender, drooping, with thin, whip-like tips. Branchlets cylindrical, nearly quadrangular, branching in whorls. Shoots in a single plane. Leaves scale-like, closely appressed, obtuse, dark green, often with a small dorsal furrow. Male cone subglobular, 5-6mm long. Female cones globose or elliptic, grouped on very short stalks, 10-20 mm across, green or purple when young, later turning dark brown, composed of 6-8(10) scales, with a small central depression and a small, triangular, reflexed mucro. Seeds 6-8 to each scale, red-brown. Cones appear in February-March, seed matures in May-June. Wood is pale yellow with pale brown heartwood, hard and durable (Vidakovic 1991, FIPI 1996).
Distribution and Ecology
W. Himalaya at 1800-300 m on limestone substrates; China: W Sichuan, in arid areas at 1500-2500 m (Vidakovic 1991); and Vietnam, where restricted to a narrow area of the Central Region and the North at elevations of 800-1200 m in Lang Son and Tuyen Quang. Also planted in Kon Tum and Lam Dong. It is a shade intolerant species, thriving in tropical and subtropical rainforests, where it prefers calcareous substrates. It occurs naturally as a dominant in mixed stands with Markhamia stipulata and Burretiodendron hsienmu, sometimes forming pure stands on mountain slopes and summits. It is rather slow-growing, and natural regeneration is very limited.
Hardy to Zone 8 (cold hardiness limit between -12.1°C and -6.7°C) (Bannister and Neuner 2001).
Listed as threatened/endangered in Vietnam by the WCMC (2001). As an endangered species; it needs protection in its remaining natural distribution area in Lang Son and Tuyen Quang provinces, and plantations should be established to preserve the gene resource for further development of this species (FIPI 1996).
Cupressus lusitanica seedlings have been extensively planted in Cupressus torulosa habitat by Indian forestry departments. The taxa hybridize, with the result that pure C. torulosa forests only remain in a few areas (Gaurav Verma pers. comm. 2019.05.28).
Remarkable Specimens
A tree in Yatton Park, Tauranga, New Zealand was measured in 2002 at 154 cm dbh and 36.9 m tall (Robert Van Pelt e-mail, 2003.01.27). I have not seen any data for specimens in their native range.
Ethnobotany
It is a prime timber with straight grain and fine texture, resistant to termites and insects. Used for cabinetwork, office furniture, fine art articles. Also used in construction and railway carriage-making. The wood is aromatic, especially the root-wood, and an essential oil extracted from these parts is used in medicine to cure inflammatory wounds, or as an antiseptic, and is also used for cosmetics (FIPI 1996). It serves as an ornamental in Yugoslavia (Vidakovic 1991),
and presumably elsewhere in the West.
Observations
Vladimir Dinets (E-mail, 2004.11.14) found it growing along the trail to Nanga Parbat Base Camp. "The trailhead is accessible from Gilgit by a hired jeep, or from Raikot Bridge on the Karakoram Highway by hitchhiking (early morning only). Near the trailhead are some Pinus gerardiana, Juniperus semiglobosa and Cupressus torulosa." See Dinets (2004) for further detail.
Remarks
Citations
Dinets, Vladimir. 2004. Ramadan in Pakistan. http://dinets.travel.ru/eibex.htm, accessed 2004.11.28, now defunct.
D. Don in Lambert. 1824. Descr. Pinus 2:18.
[WCMC] World Conservation Monitoring Centre. The Socialist Republic of Viet Nam
Appendix 5 - Threatened Plant Species. http://www.wcmc.org.uk/infoserv/countryp/vietnam/app5.html, accessed 2001.11.25, now defunct.
See also
Elwes and Henry 1906-1913 at the Biodiversity Heritage Library. This series of volumes, privately printed, provides some of the most engaging descriptions of conifers ever published. Although they only treat species cultivated in the U.K. and Ireland, and the taxonomy is a bit dated, still these accounts are thorough, treating such topics as species description, range, varieties, exceptionally old or tall specimens, remarkable trees, and cultivation. Despite being over a century old, they are generally accurate, and are illustrated with some remarkable photographs and lithographs.
Farjon (2005) provides a detailed account, with illustrations.







