
A 1000 yr old tree (980 years ring count) from Val Malenco, Italy [Renzo Motta].

A large tree in habitat, above Courmayeur, France [Brad Cadwallader, 2019.08, post to Facebook "Planet Conifer" group].

A tree in habitat, Valfloriana, Italy, elev. 1800 m [Nicolò Gaetani, 2019.10.25].

Cones and foliage on an ornamental of var. polonica [C.J. Earle, 2004.04.03].

Ripening cones on an ornamental of var. decidua [C.J. Earle, 2004.06.07].

Foliage and ripe cone on a tree in habitat, Valfloriana, Italy, elev. 1800 m [Nicolò Gaetani, 2019.10.25].

Bark on a 50 cm dbh ornamental tree, Seattle (USA) [C.J. Earle, 1999.03].

Pinus cembra (dark green) and Larix decidua (light green) in a mountain valley, 1200-1500 m elevation, along the Tour du Mont Blanc, France. Each species primarily forms pure stands, with cembra prevalent in rocky areas and decidua prevalent on deeper soils. Note avalanche tracks [Réjean Drouin, 2017.07].
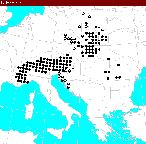
Range of Larix decidua (Atlas Florae Europaeae 1998).

Larix decidua
Miller
Common names
European larch; Mélèze d'Europe [French]; larice comune [Italian]; Gemeine Lärche, Europäische Lärche [German]; Modřín opadavý [Czech]; Smrekovec opadavý [Slovakian];
Modrzew europejski [Polish]; Модрина європейська [Ukrainian]. Var. polonica: Larice, zada [Polish].
Taxonomic notes
Syn: Pinus larix L.; Larix europaea Lam. & DC.; L. sudetica Domin (Farjon 1990). Two varieties, besides the type:
- Larix decidua var. polonica (Racib.) Ostenf. & Syrach Larsen (syn: L. polonica Racib.; L. decidua ssp. polonica (Racib.) Domin).
- Larix decidua var. carpatica Domin (syn: L. carpatica Domin).
The hybrid of L. decidua and L. kaempferi is Larix × marschlinsii. This hybrid, which arises when the trees are planted near each other, almost alway shows L. decidua as the pollen donor and L. kaempferi as the seed parent. The hybrids show high heterosis (hybrid vigor) (Eckenwalder 2009).
Description
Deciduous tree to 30(-52) m tall and 100(-270) cm dbh, usually with a single round trunk supporting a pyramidal to columnar crown of thick, downswept branches, ascending near the ends. Bark deeply fissured, flaking, medium to dark gray to reddish brown, with reddish inner bark. Twigs slender to stout, flexible to stiff, pale yellow to tan, glabrous or very slightly pubescent, the stubby short shoots cylindrical and 3-10 mm long. Leaves on long shoots sparse, appressed to the shoot or spreading; most leaves borne on short shoots in bunches of 30-40 needles, 2.5-3.5 cm long, 0.5-1 mm thick, linear, soft, pliable, flattened or broadly triangular in cross-section, with some stomata on all surfaces but mostly on the lower surface, in two pale bands separated by a keel; light green, darkening through the summer, turning yellow and falling in autumn; apex obtuse to acute. Pollen cones terminal on short shoots, yellow, 5-10 mm long. Seed cones terminal on short shoots, on curved peduncles 5-10 mm long, ovoid with an obtuse apex, 2.5-4 cm long, comprised of 25-35 seed scales, bracts shorter than seed scales; dark red maturing pale green, then bark brown. Seeds 4 mm with a 6-10 mm wing (Farjon 1990, 2010; pers. obs. of ornamental trees).
Distribution and Ecology
SE France, Switzerland, N Italy, S Germany, Austria, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Poland, Ukraine, and Romania; in the Alps and the Carpathian Mountains at (600-)1000-2200(-2500) m (Farjon 1990). Hardy to Zone 4 (cold hardiness limit between -34.3°C and -28.9°C) (Bannister and Neuner 2001, variety not specified).
Variety carpatica is in the E Carpathian Mountains and in the NW Ukraine (Farjon 1990).
The IUCN has not assessed the type variety or var. carpatica for conservation status, but in view of their wide distributions, they would likely rank as "least concern." Var. polonica had an extremely limited distribution and a poor prognosis when it was assessed as "endangered" in 2011 (Farjon 2013, accessed 2022.03.20); it is now more likely "critically endangered."
Remarkable Specimens
A tree 271 cm dbh and 30 m tall was recorded in the Ulten Valley, Saint Nicholas, Italy (International Dendrology Society Year Book 1984).
There is also a record of a tree 261 cm dbh and 28 m tall in Santa Geltrude in the Trentino Alto, Ultimo, BZ, Italy (Corpo Forestale Della Stato, a listing of big trees in Italy, link now dead).
A tree found by Räsänen (2010) was then 46.8 meters tall (laser measurement) and 149 cm dbh, in Thüringen, Germany, outside the natural range of the species.
Another big German tree is the Brüsenwälder Lärche, planted in about 1770 and located near Warthe, north from Berlin, Brandenburg. It was 46.3 m tall (laser) and 152 cm dbh in 2010 (Räsänen 2010).
Another stand of very large trees, planted outside the native range of the species beginning in about 1742, is in Schlitz, Germany. One celebrated tree called the "Grand German" is 112 cm dbh and 45.5 m tall (Räsänen 2012). Another tree in the stand was 53.8 m tall (laser) and 80 cm dbh on January 10, 2013; this is currently the tallest known tree in the species (Brüne 2013).
The tallest tree in Finland is a 47.1 m (laser) tree in a research forest of the Finnish Forest Research Institute in Punkaharju (Räsänen 2012).
The oldest tree is documented by one tree-ring collection, presumably based on living-tree material, that covers 986 years (International Tree-Ring Data Bank, chronology FRAN010, limiting dates 988-1974). The tree pictured at right yielded a 980 year ring count that did not go to pith (Renzo Motta, pers. comm. 2000.07.01).
Ethnobotany
This is an important timber tree in Europe, where extensive plantations have been created, primarily at elevations substantially lower than the montane and subalpine native distribution of the species.
Some interesting dendrochronology studies involving the ecophysiology of ring development have been done by Oleksyn and Fritts (1991).
Observations
Remarks
The epithet refers to the deciduous leaves.
Var. polonica is listed as vulnerable on the IUCN Red List.
Citations
Atlas Florae Europaeae. 1998. Computer program formerly available for download at http://www.fmnh.helsinki.fi/english/botany/afe/index.htm, accessed 2009.04.17, now defunct.
Brüne, K. 2013. European larch close to Richthof. www.monumentaltrees.com/en/deu/hesse/vogelsbergkreis/4524_richthof/10650/, accessed 2013.02.24.
Farjon, Aljos. 1990. Pinaceae: drawings and descriptions of the genera Abies, Cedrus, Pseudolarix, Keteleeria, Nothotsuga, Tsuga, Cathaya, Pseudotsuga, Larix and Picea. Königstein: Koeltz Scientific Books.
Miller, P. 1768. The Gardener's Dictionary, ed. 8. London. Available: botanicus.org/title/b12066618, accessed 2011.05.20.
Räsänen, K. 2010.10.20. European larch. www.ents-bbs.org/viewtopic.php?f=198&t=1533, accessed 2012.09.20. The site includes a number of photographs of tall and big larches.
Räsänen, K. 2010.10.20. New record European larch. http://www.ents-bbs.org/viewtopic.php?f=198&t=4538&p=19287#p19281, accessed 2012.09.20. The site includes some excellent photographs of these trees.
See also
Elwes and Henry 1906-1913 at the Biodiversity Heritage Library (as L. europaea) (Photos). This series of volumes, privately printed, provides some of the most engaging descriptions of conifers ever published. Although they only treat species cultivated in the U.K. and Ireland, and the taxonomy is a bit dated, still these accounts are thorough, treating such topics as species description, range, varieties, exceptionally old or tall specimens, remarkable trees, and cultivation. Despite being over a century old, they are generally accurate, and are illustrated with some remarkable photographs and lithographs.
FEIS database.
The species account at Threatened Conifers of the World.









